The BlotCycler™ In Action: Report of a Western Blot Application note
Improved detection of EPO in blood and urine based on novel Velum SAR precast horizontal gels optimized for routine analysis
Dirk Schwenke
Institute of Doping Analysis and Sports Biochemistry Dresden, Kreischa, Germany
Blood doping is the misuse of certain techniques and/or substances to increase one’s red blood cell mass, which allows the body to transport more oxygen to muscles and therefore increase stamina and performance.
There are three widely known substances or methods used for blood doping, namely, erythropoietin (EPO), synthetic oxygen carriers and blood transfusions. Each is prohibited under WADA’s List of Prohibited Substances and Methods.
For the detection of genetically and chemically modified EPO, and detection of micro-dose EPO, a further improved detection method is required.
The main focus of the present study was to establish the SAR-PAGE as a routine method according the new technical document WADA-TD2014EPO.
Materials and methods
Materials
Pharmaceutical formulations of recombinant and biotechnologically as well as chemically modified erythropoietins were obtained from the manufacturers Roche (NeoRecormon, MIRCERA; Mannheim,
Germany) and Amgen (NESP; Thousand Oaks, CA).
The standard for human recombinant erythropoietin (rhEPO; BRP-EPO batch 3) were obtained from the National Institute for Biological Standards and Control (NIBSC, Hertfordshire, UK).
Blood was collected in Vacuette K2E tubes and Vacuette Z Serum Sep Clot Activator tubes, both purchased from Greiner Bio-One GmbH (Kremsmünster, Austria).
Devices for microfiltration (Steriflip (0.2 μm), polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membranes (Immobilon-P) and Immobilon Western HRP Substrat were purchased from Millipore (Billerica, USA). 10 x PBS-stock solution were from LONZA (Rockland, ME). Tris hydrochloride, Dithiothreitol (DTT), milk powder (blotting grade) were obtained from Roth (Karlsruhe, Germany).
The primary antibody used, mouse anti-human EPO antibody (Clone AE7A5), was obtained from R&D Systems (Oxford, United Kingdom). The used secondary goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L), conjugated with a horseradish peroxidase was purchased from Pierce (Rockford, IL).
The EPO purification kit containing anti-EPO monolith columns, UPD (Urine Precipitate Dissolvation) buffer, sample dilution buffer, exposure aid, desorption buffer and adjustment buffer were obtained from MAIIA Diagnostics (Uppsala, Sweden). Velum SAR gels (24, 30 and 40 slot wells, 10% T, 0.5 mm) were obtained from NH DyeAGNOSTICS (Halle, Germany) in cooperation with Electrophoresis Development & Consulting (Tübingen, Germany).
The isoelectric focusing (IEF) of all samples was performed by using a IEF-KIT from Serva (Heidelberg, Germany).
The incubation and wash process was carried out with the BlotCycler™ (Mansfield, MA).
Methods
In this study the doses of rEPO were reduced to an absolute minimum, yielded in a very low hematological response.
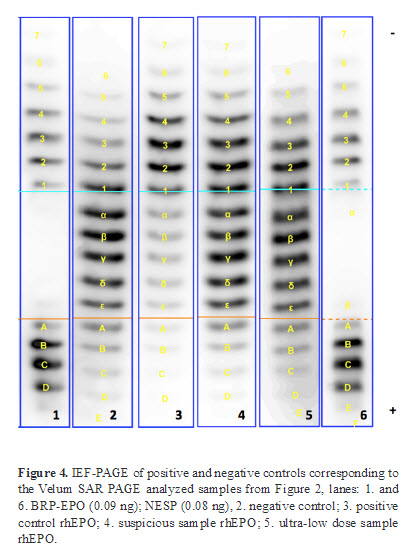
In order to evaluate the performance of the EPO analysis based on the Velum SAR precast gels positive and negative controls as well as a suspicious rhEPO and an ultra-low dose rhEPO were analyzed by IEF-PAGE and the novel Velum SAR PAGE.
These four samples served as a control for the IEF method. Furthermore, the profiles of positive and negative controls serve as a reference in order to screen for suspicious profiles (Figure 4).
Conclusions
According to the WADA Technical Document 2014EPO, the initial testing procedure for the detection of doping should be done by IEF or SAR-PAGE.
When the two methods were compared, in the IEF method, the detection windows were up to 12 hours longer, with a very individual response.
This research suggests that the detection of mixed bands consisting of endogenous EPO and rEPO using Velum SAR PAGE shows a much better performance for detecting low dose doping than the IEF method does.
With the adoption of the horizontal SAR-PAGE in combination with the precast film-supported Velum SAR gels, the discriminatory capacity of micro-dose application of rEPO was significantly enhanced.
The additional benefits of the this method in Western blot application were the easier handling of the Velum gels compared to the NuPage gels and, in combination with the BlotCycler™, the automating of the time consuming washing and incubation process.